Develop Cypress end-to-end tests on Gitpod.io - Virtual Desktop included
Experience it for yourself
Before we go into the details, you can experience Cypress end-to-end tests running in a virtual environment in your browser with the following link:
https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/mootoday/cypress-on-gitpod
Click the ”Login with GitHub & Launch Workspace” button, follow the instructions and you will be up and running in a moment.
Once npm install completes automatically, a development server starts in one terminal and Cypress starts in a second terminal. Besides that, a second browser tab will open with a virtual desktop where, after a minute or so, you will see the Cypress UI.
The first browser tab shows the editor (the errors in the console can safely be ignore):
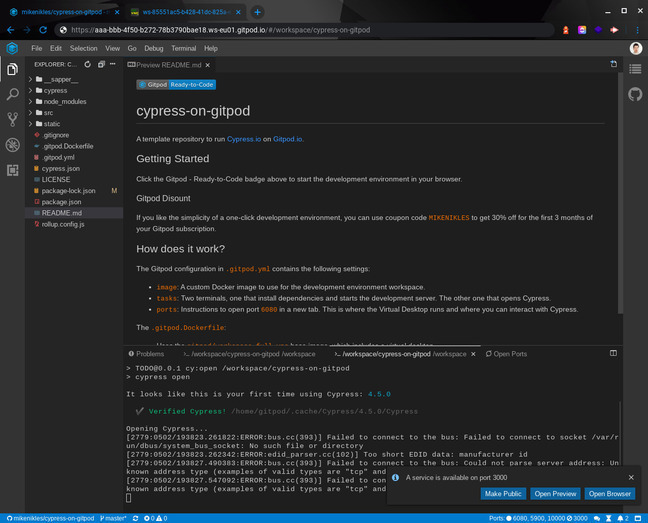
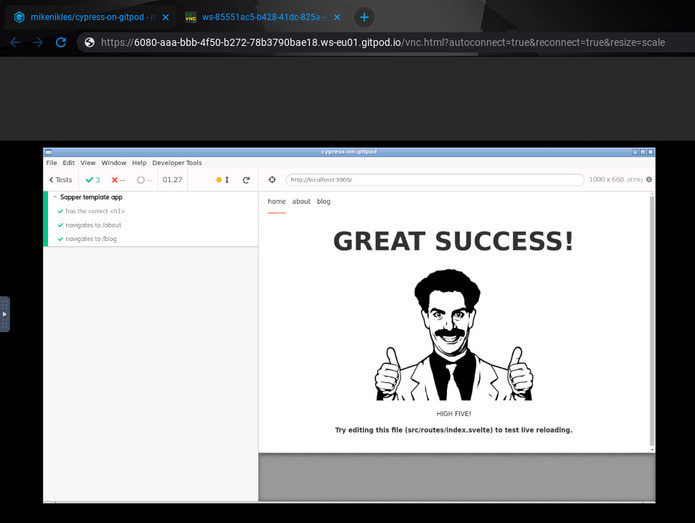
Whereas the second browser tab provides the Cypress UI (in this case, it’s a default Sapper application):
What is required to make it work? (Pull Request)
The source code is available at https://github.com/mootoday/cypress-on-gitpod.
The first thing is to add cypress as a dev dependency with npm i -D cypress. This ensures it gets installed like any other dependency when npm install runs.
Gitpod configuration
Next, we need a .gitpod.yml configuration file to configure a custom docker image (more on that in a minute), a few tasks to run when the development environment loads and some port definitions. Let’s look at that file section by section:
image:
file: .gitpod.DockerfileThis instructs Gitpod to use a custom Docker image, as defined in the specified file.
tasks:
- init: |
touch /tmp/.npm-lock
npm install
rm /tmp/.npm-lock
command: npm run dev
- init: sleep 1 && while [ -f /tmp/.npm-lock ]; do sleep 1; done
command: npm run cy:openThe two tasks (as seen by their -) tell Gitpod to open two terminals. In the first terminal, a temporary file is created, npm install executed and eventually, the temporary file is deleted.
In the second terminal, the init command waits until the temporary file is no longer available. When that’s the case, we can be sure npm install completed in the first terminal and all dependencies are available. We then open Cypress with the provided cy:open NPM script.
To wrap up the .gitpod.yml file, we define three ports and instruct Gitpod what to do. 5900 and 10000 are ignored, 6080 is opened in a new tab - that’s the virtual desktop.
ports:
- port: 5900
onOpen: ignore
- port: 6080
onOpen: open-browser
- port: 10000
onOpen: ignoreA custom Docker image
As defined in the .gitpod.yml configuration above, we define a custom Docker image in .gitpod.Dockerfile as follows:
FROM gitpod/workspace-full-vnc
# Install Cypress dependencies.
RUN sudo apt-get update
&& sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y
libgtk2.0-0
libgtk-3-0
libnotify-dev
libgconf-2-4
libnss3
libxss1
libasound2
libxtst6
xauth
xvfb
&& sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*We use a base image provided by Gitpod. Next, we install the dependencies required by Cypress as documented.
Conclusion
A few lines of configuration and we’re up and running with Cypress on Gitpod.io. Make sure you have a look at the pull request where I provided a few annotations in the code.
👋
